Bitrate - a characteristic of the speed of the flow of video andor audio information. It is measured in thousands of kilo-bits per second. The more bitrate there is, the more space on the disc is occupied by this information. Bitrate of 8000 kbit/s corresponds to 1 mega-byte per second. For example, for 60 seconds of video, coded with bitrate 8000 kbit/s, 60 mega-bytes are occupied on the disc.
Cell - in DVD-video the minimum addressed DVD element of a project. If a film is broken into the chapters, for example, that fragment from the beginning of chapter to its end is a cell.
Constant Bit Rate (CBR) - term that is used for describing the parameters of coding in a number of MPEG versions. It indicates that during the coding into an MPEG, the Bitrate is always constant and does not depend on the content of the coded video information.
Dolby Digital AC-3 - in the general terms the system of coding (compression of) sound, developed by the engineers of Dolby Laboratories. A Dolby Digital Soundtrack can contain mono sound, stereo sound, and also 5.1 sound, recording and playback of which is carried out for 6 channels - left, centre and right front channels, low-frequency LFE (conventionally called the subwoofer) and also left and right rear channels.
Dolby Pro Logic - the system of stereophonic sound, developed by the engineers of Dolby Laboratories. Recording and playback of sound is carried out for five channels - left, centre and right front channels, and also left and right rear channels. It differs from the Dolby Surround system in terms of the large separation between the front and rear channels.
Dolby Surround - one of the first systems of stereophonic sound developed by engineers at Dolby Laboratories. Recording and playback of sound is carried out for four channels - left and right front channels, and also left and right rear channels. The signal for the rear channels is coded together with the signals for the front channels. During playback the stereo signal requires decoding for the extraction of the information for the rear channels.
Dynamic Range - a quality coefficient of audio. It is measured in decibels and the ratio of the output signal level with the nominal output power to the level of the smallest audible sound shows. Such parameters as dynamic range and the Signal/Noise Ratio are connected together - there cannot be in the device a high relationship between the signal/noise and a narrow dynamic range. For high-quality audio devices the dynamic range value cannot be worse than 95 dB.
Dynamic Range Compression (DRC) - an adaptation in DVD players with their own sound decoders and receivers. The compression (or decrease) of the dynamic range limits the peaks of sound within the film. If a viewer desires to watch a film in which they are possible abrupt changes in the loudness level (a film about the war, for example), but he does not want to disturb other members of his family, DRC could be used. It is rumoured that after starting DRC the low frequencies and high-pitched sounds lose transparency, therefore DRC is not worth using unless necessary.
DV - Digital Video - a type of videodata utilized for the exchange of video between digital video cameras, video tape recorders and computers. The transport interface IEEE-1394 (FireWire) is usually used for transferring DV. In DV the fixed contraction coefficient of video signal 5:1 and, accordingly, flow is 3.515 MBytes/s. Resolution for PAL is 720x576, for NTSC 720x480. The recording supports sound reproduction along 4 channels with a discrete frequency of 32 kHz and the word length of 12 bits, or along 2 channels with a discrete frequency of 48 kHz and the word length of 16 bits. In DV the compression is used intraframe, with which each sequence is compressed by itself, without taking into account information in the adjacent personnel, so interfield compression, using the analysis of static images in the adjacent fields with the use of an identical background for the adjacent images. Such compression algorithms give a very insignificant quantity of artifacts.
DV Type-1 - Digital Video Type-1 - the original (native) version of DV, completely incompatible video for Windows and supported only through DirectShow. Flow (file) size Type-1 contains video and audio (stereo, 48 kHz, 16 bit) in one flow, i.e. with alternating video and audio. Specifically, this type is recommended for the capture and subsequent working on video DV on the computer.
DV Type-2 - Digital Video Type-2 - the old version DV type, conversely compatible with Video for Windows, it can read the file of type Type-2 (but it can not preserve in it without the special codec). The flow (file) of type Type-2 contains video, also, from one to four flows (channels) for the audio (maximally 2 stereos-channel, on 32 kHz, 12 bit each). In comparison with Type-1 it requires high expenditures for decoding and mixing, therefore the field of application of this type gradually, in proportion to the processing of the programs playing videos of type Type-1, will be reduced.
DVD - Digital Versatile disc - a contemporary standard of information storage on the optical (laser) disc. It differs from the the usual CD-Rom in terms of the increased capacity, almost 30 times (to 17 GB). For DVD is accepted another standard per unit of speed, so the volume of information on the disc is considerably more. For 1x speed it is customary to assume the rate of reading DVD of disc 1352 kBytes/sec. Therefore disc with 5x DVD by speed, for example, it has the maximum speed of readout 6760 kBytes/sec. There are available the following versions of DVD disc types:
One-sided single-layer with a capacity of 4.7 GB.
One-sided dual-layer with a capacity of 9.4 GB.
Two-sided single-layer with a capacity of 9.4 GB.
Two-sided dual-layer with a capacity of 17 GB.
There are also a number of DVD disc types depending on the designation and method of recording the information onto them:
DVD-ROM - disc, accessible only for reading; it can be read only on a DVD drive.
DVD-Video - it is used for the recording of video films and can be played back in DVD drives in computers, and in DVD players.
DVD-R, DVD+R - single use discs - are intended for the single recording of data. Capacity of 4.7 GBytes. discs are compatible with most DVD-video players and DVD-Rom drives in computers.
DVD-RW, DVD+RW - repeated use discs - are intended for repeated recording of data. Capacity of 4.7 GBytes. discs are compatible with most DVD-video players and DVD-Rom drives in computers.
DVD-RAM - repeated use DVD discs, incompatible with most DVD-video players and DVD-Rom computer drives.
DVD-Audio - a new standard to audio discs - due to the increased capacity of DVD discs the discrete frequency is increased to 48/96/192 kHz (also 44.1/88.2/176.4 kHz) and word length to 16/20/24 bits.
DVD-1 - the code name of the first generation of DVD disc drives. They have an average read speed not above 8x, and, in addition to this, they cannot read CD-R and CD-RW discs.
DVD-2 - the code name of the second generation of DVD disc drives. They have an average read speed of 24x, and, in addition to this, they can read CD-R and CD-RW discs.
DVD Structure - structure of DVD-video disc. Structure of a DVD-video disc is shown in the figure:
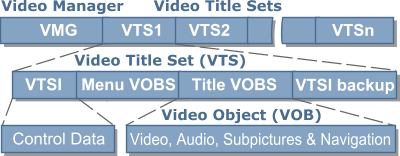
Linear PCM - type of uncompressed (i.e. without the loss of quality) sound, utilized for the sound recording into some DVD-video discs. It differs from PCM sound on most audio CDS in terms of the high discrete frequency from 48 to 96 kHz and in terms of word length 16, 20, or 24 bits. This type is used in essence only on musical DVD-video discs. The wide use of this type in DVD-video discs is prevented by its high bitrate (in other words, sound in this type occupies too much place), minimally about 1500 kbits.
Motion Menu - menus in DVD-video discs, that use a video background.
Multi-angles - displaying the same image, taken by different cameras. This possibility is placed into the standard of the DVD-video disc, but in practice is rarely used. This is explained by the fact that too much space on the disc is required by each video angle and, in addition to this, by the additional expense during the photographing of the film itself
PGC - Program Chain - Basic element of the content structure of DVD-video discs, it consists of several programs, connected together for the sequential playback. On a DVD-video disc there must be at least one PGC.
Program - by program in the DVD medium it is understood to mean a collection of audio and video fragments. It includes several cells.
PTT - Part of Title - part of a title, in other words a chapter or scene.
RF modulation - Radio Frequency Modulation - in the days of the record players and laser videodiscs digital sound was transferred from such record players to the amplifier in the frequency-modulated form. In many modern DVD players there is a possibility of the inclusion of sound in the same form for the compatability with different amplifiers (receivers).
Seamless playback - the passage inside the program without interruption in the reproduction of video.
Slide Show - the sequential demonstration of static images by the DVD by player, the duration of each image is determined by the DVD authoring program during creation. Together with the pictures it is possible to add an audio track.
Still Menu - menus on DVD-video discs that have no moving elements.
Still Show - the sequential demonstration of static images by DVD players. It differs from Slide Show by the fact that the images change only after using the buttons on the DVD player and Still Shows cannot have an audio track.
Subpicture - on DVD-video discs they are the basic method of creating those elements of the menu which can change its view on the screen depending on the actions of user. Creating a subpicture in a DVD-Authoring program, the author of the DVD-video disc indicates how the DVD player must map onto the screen the control elements of the DVD-video menu. In the simplest of DVD-Authoring programs the subpicture is created by the program itself, therefore in such programs limits in the options available to the author in the development of the menu are inevitable.
Title - greatest layout element in the DVD-video disc.The DVD-video disc can contain up to 99 titles, title selection is possible through the menu.
Variable Bit Rate (VBR) - a term used for describing the parameters of coding in a number of versions of types of MPEG. In contrast to CBR the speed of the output flow MPEG of coder will depend on the content of the coded video material. As a rule, with use VBR of a regime to coder they are indicated average, the maximum and minimum speed of flow. In this case the coder selects the optimum speed of flow in the dependence on the dynamics of the concrete fragment of film, preserving the average speed of the flow of constant. Since regime VBR makes it possible to decrease the size obtained MPEG file without the damage for its quality, it adapts in the overwhelming majority of the cases for coding of films for DVD-video discs. Regime CBR adapts only for coding of short films, which and with the highest speed of flow are placed to DVD-video disc.
VMG - Video Manager - disc menu, serves as access to all the titles on the disc. Nevertheless if there is only one VTS on the disc it can not actually be used. If there is more than one VTS, only through the VMG is it possible to obtain access to any VTS.
VTS - Video Title Set -
the container for practically all the components of the DVD-video disc.
Specifically, inside the VTS are established strict limitations on the unified
standard of the files used. It can contain to 99 titles.